Tape measure: guidelines, certification & calibration accuracy

In professional construction, mechanical engineering, and technical trades, measurement accuracy is of critical importance. The tape measure, often also called a measuring tape or distance measurer, is one of the most commonly used hand tools. Although choosing a tape measure may seem trivial, there are strict guidelines regarding tolerances, calibration, and certification that ensure reliability and compliance with legislation.
What is a tape measure and how it is used
A tape measure is a basic tool for measuring distances, usually made of a metal strip wound into a housing. It is most commonly marked in meters, centimeters, and millimeters. Tape measures are used for:
- measuring longer distances or areas where the precision of digital measuring devices is not required,
- quickly checking dimensions on construction sites or in manufacturing,
- use in combination with other measuring instruments such as spirit levels or laser measurers.
Professionals must pay attention to the length, width, and material of the tape, as these factors affect bending, stretching, and consequently the accuracy of the measurement.
Tape measure tolerances: what they mean
Every tape measure has defined tolerance values that are legally regulated and standardized. Tolerance indicates the maximum permissible deviation from the nominal length:
- For tape measures up to 5 m, tolerance values are usually ±1 mm,
- for tape measures longer than 20 m, the tolerance increases with length, e.g. ±3 mm,
- on professional tape measures, tolerance values are clearly marked on each tape.
Tolerance directly affects measurement accuracy and is crucial in construction tolerances, where every millimeter matters. It should be noted that longer and thinner tapes generally achieve lower accuracy due to stretching and curvature.
Accuracy classes of tape measures – Roman numerals I, II, III
On every professional tape measure, you will usually find Roman numerals I, II, or III, which indicate the accuracy class or tolerance of the measuring tape. This is not just a symbol—it is an official classification of accuracy for which the tape measure has been tested and certified in accordance with European standards. Such marking means that the manufacturer has tested its tape measures under specified conditions and confirmed that their deviations do not exceed the permitted tolerances for the respective class.
Understanding the classes:
- Class I (I): the most accurate – the smallest permissible deviation between actual and nominal length.
- Class II (II): medium accuracy – the most common professional class, suitable for most construction and technical applications.
- Class III (III): the least accurate – allows the largest deviation, suitable only for non-commercial or non-critical measurements.
The accuracy class, marked with Roman numerals, is often shown on the tape together with other information (e.g. tape length, country of origin, year of manufacture) and represents the maximum permitted tolerance deviations under standardized conditions (temperature ~20 °C and standard tape tension).
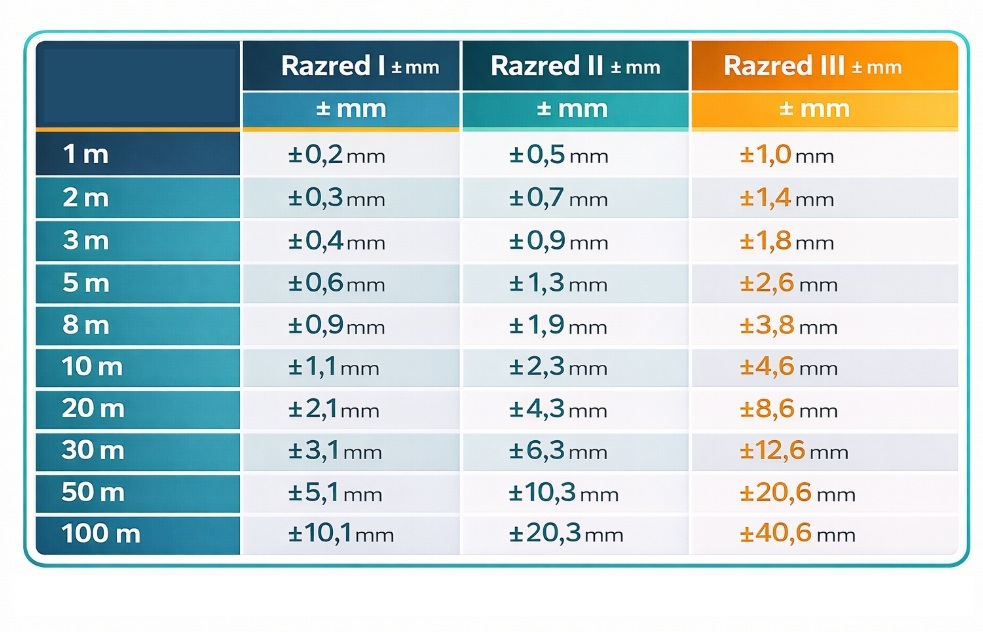
Table of tolerances by length and accuracy class
The table below shows the permitted deviations (± mm) for the three main accuracy classes at different tape lengths. This means that the actual length may be greater or smaller than the nominal length by this value, and this is legally defined and certified.
Calibration of tape measures: why it matters
Calibration means that a tape measure has been verified against a reference length standard recognized by national metrology institutions. Calibrated tape measures have:
- a calibration certificate proving compliance with standards,
- assurance that the measuring tool is accurate within the declared tolerances,
- often systematic markings such as serial numbers and the calibration date.
In practice, this means that companies can use calibrated tape measures for legal, construction, or technical measurements where proof of the measuring instrument’s accuracy is required. Users of POPAR tape measures can rely on their measurements being compliant with standard requirements.
Certification and standards for tape measures
In the EU, tape measures fall under the category of measuring instruments subject to the requirements of the European Measuring Instruments Directive (MID, 2014/32/EU). The MID defines the conditions and procedures for the conformity of measuring instruments and their free movement on the EU market.
Choosing the right tape measure
When selecting a tape measure for professional use, consider the following:
- Tape length and width – longer tapes have higher tolerances, while wider tapes are more stable.
- Tape material – steel, fiberglass, or combinations with anti-corrosion treatment, which affect bending behavior and service life.
- Housing and ergonomics – a durable housing with soft inserts improves grip and reduces fatigue during prolonged use.
- Calibration certificate – essential for demanding professional applications where proof of accuracy is critical.
- Tolerances – check whether the tape measure complies with standards for the lengths you measure daily.
POPAR tape measures are designed to meet applicable standards and provide reliable accuracy for everyday professional use.
Maintenance and proper use of tape measures
For long-term accuracy, it is recommended to:
- regularly inspect and clean the tape,
- protect it from impacts, dust, and moisture,
- store it properly to prevent twisting or damage,
- perform regular calibration for tape measures used in legal or contractual measurements.
With proper maintenance, a tape measure remains accurate, reliable, and safe to use on any construction site or in the workshop.
A tape measure is not just a basic hand tool—it is a key measuring instrument that ensures accuracy and reliability in professional environments. Understanding tolerances, calibration, and certification is essential for anyone who regularly uses measuring tools. POPAR tape measures ensure compliance with European standards, robust design, and the level of accuracy professionals need for everyday work. By choosing the right tape measure and following maintenance guidelines, you can ensure that measurements are always reliable and precise.